The most common infection that affects nearly 90% of people on earth is called HPV or human papillomavirus. When a papilloma is discovered, no one alarms, because in folklore it is considered an ordinary wart. Remove them only if they interfere or present a cosmetic defect. The disease is "human" and is transmitted only from sick people to healthy people: in everyday life, through contact, through the reproductive system, during childbirth from mother to child. The disease can manifest on the skin or mucous membranes as warts, papillomas, or cysts. Let's find out what is the HPV virus and how dangerous it is to humans?
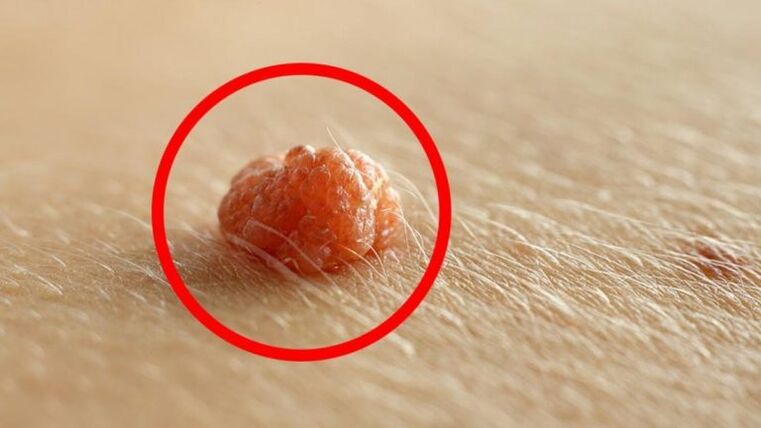
What is HPV?
Viruses live in most people. HPV is so small that it can enter the bloodstream through scrapes, scrapes, and small cuts in the skin. It may not show up in any way during the carrier's lifetime, or it may continually manifest in all its glory. The incubation period can range from a few weeks to several years. The signal for action is a weakening of the immune system. If papillomas appear on the skin and mucous membranes, the body needs urgent treatment.
There are more than 70 types of human papillomavirus, but several new strains are registered every year. Generally, all types of HPV infections can be divided into two groups.
Warts are viruses that cause the growth of warts on the body.
- HPV types 1, 2, 3, 4 cause the formation of warts or nodules;
- HPV types 3, 10, 28, 49 cause flat warts;
- HPV type 27 forms "flesh warts";
- HPV: 5, 7, 10, 12, 14, 15, 17, 19-24, 26, 27, 29, 57 - also develop warts.
Papilloma - the virus that causes the formation of papillomas and warts.
- HPV 6, 11, 13, 16, 18, 31, 33, 31, 33, 58, 52, 39, 70, 30, 40, 42, 43, 51, 55, 57, 59, 61, 62, 64, 67-69
What is the danger of HPV?
Why have doctors been sounding the alarm for the past few years and trying to educate the public about HPV? Because the percentage of cancer patients diagnosed with this virus is increasing seriously. Not only women get uterine cancer, but also men get cancer of the male reproductive organs. The number of skin cancers in the elderly is also on the rise.
Of course, there are types of HPV that do not affect the internal health of a person, but their manifestation in the form of papillomas and growths of warts is annoying. They are classified as low carcinogen - minimal risk of developing cancer. Such formations can be easily eliminated by folk methods or cosmetic medicine. But the virus itself is not treated with any means and drugs. If a person is infected, then that person will be a carrier of the virus for life.
Other subspecies of papillomavirus infections belong to the group of highly carcinogenic, i. e. they can affect the formation of malignancies in the body.
There are 3 types of its carcinogenic potential:
- Low cancer risk HPV: 6, 11, 40, 42, 43, 44, 54, 61, 70;
- HPV average cancer risk: 26, 31, 33, 35, 51, 52, 53, 58, 66;
- High-risk HPV: 16, 18, 36, 39, 45, 56, 59, 66, 68.
Diseases and types of HPV
Below we provide a list of papillomaviruses.
Skin damage:
- Warts on soles (calfs) 1, 2, 4
- Common warts 2, 4, 26, 27, 29, 57
- Flat warts 3, 10, 28, 49
- Warts Butcher 7
- Veruciform epidermal dysplasia 2, 3, 5, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14, 15, 17, 19, 20-25, 36, 37, 46, 47, 50
Damage to the mucous membranes of the genital organs:
- Genital warts 6, 11, 42-44, 54
- Epithelial lesions without invasion into other layers (intraepithelial lesions) may be precancerous 62, 64, 67-70
- Cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina, anus and penis 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 54, 56, 66, 68
Lesions of non-genital mucous membranes:
- Injury to oral mucosa (focal epithelial hyperplasia) 13, 32
- Recurrent airway papillomatosis 6, 11, 30
- Malignant neoplasms of head, neck, lung 2, 6, 11, 16, 18, 30
Types of skin lesions caused by viruses
Most human papillomavirus infections have no symptoms. External manifestations of the disease are different, the following are several types:
common warts
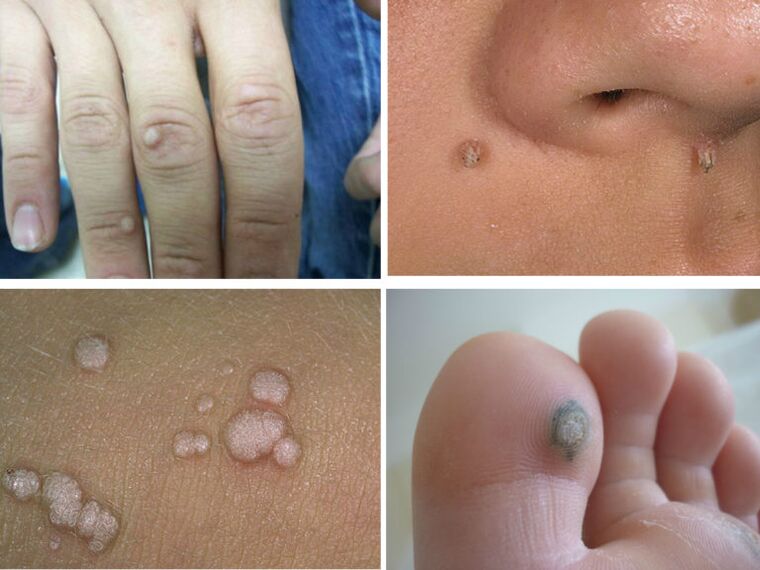
The most common form of HPV is warts. Most people can find on their body a similar papule with a diameter of no more than 5-7 mm. Usually warts are located on the outside of the palms, between the fingers, soles of the feet, chin, eyelids, and scalp. Warts can grow in size and can also form colonies from maternal papillomas. Then they can cause discomfort: itching and tingling in the places of growth.
The most "disease" is the plant wart, the common name is "thorn". When walking, they put pressure on the nerve endings causing the patient to experience severe pain. Such tumors are recommended to be surgically removed in clinics. Warts are simply not a threat to human health, they almost never develop into cancerous tumors.
Butcher's warts
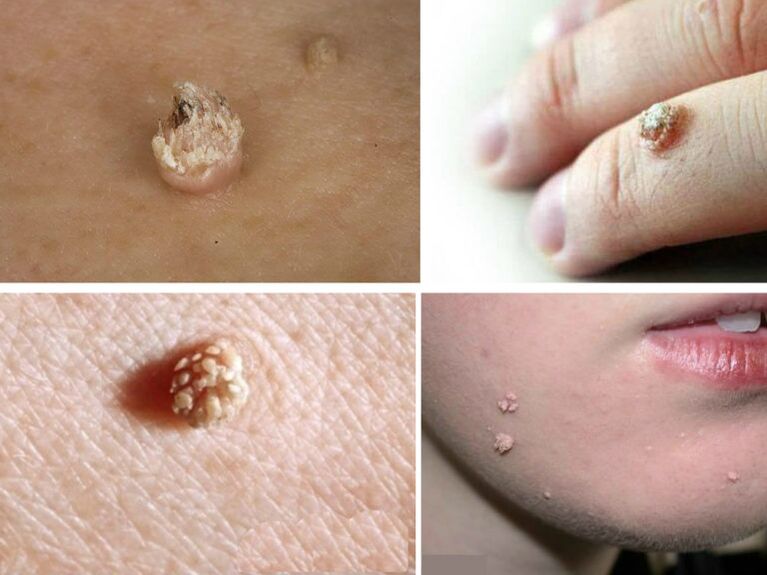
Meat warts look like many thick threads sticking out of a single wart. Usually found on the fingers, especially where there are cuts. Long fibrous papules bring inconvenience to their owners, as these shapes do not look aesthetically pleasing. They can bleed when bumped or scraped. Although such warts are safe in a cancerous sense, their damage leads to trouble. The recommendation of doctors is to remove it without fail.
flat warts
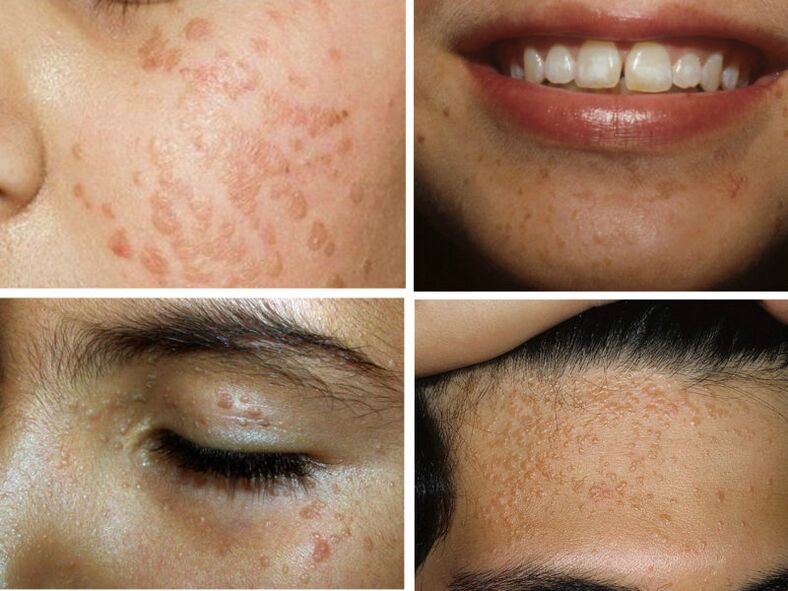
Flat warts are also known as "juvenile warts" because they usually appear during adolescence. They look like a large dry rash on the skin. Cover forehead, cheeks, chin, forearms. Color may be the same or slightly darker.
Butcher's warts
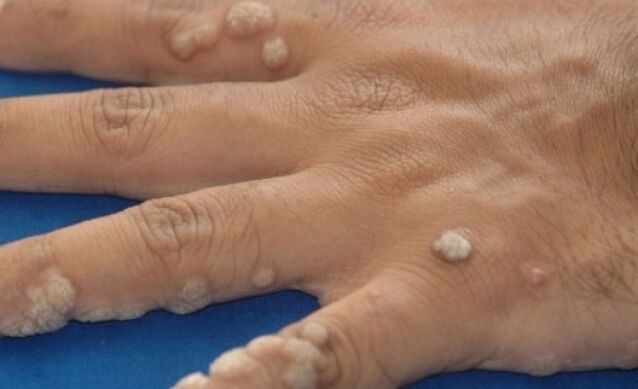
Flesh warts are scarred warts with normal skin color. They can be both singly and as a cluster of many pieces. The names of these warts are given by the professional activities of the butchers. It can be said that this type of infection is an occupational disease of the meat industry.
Verruciform epidermal metaplasia
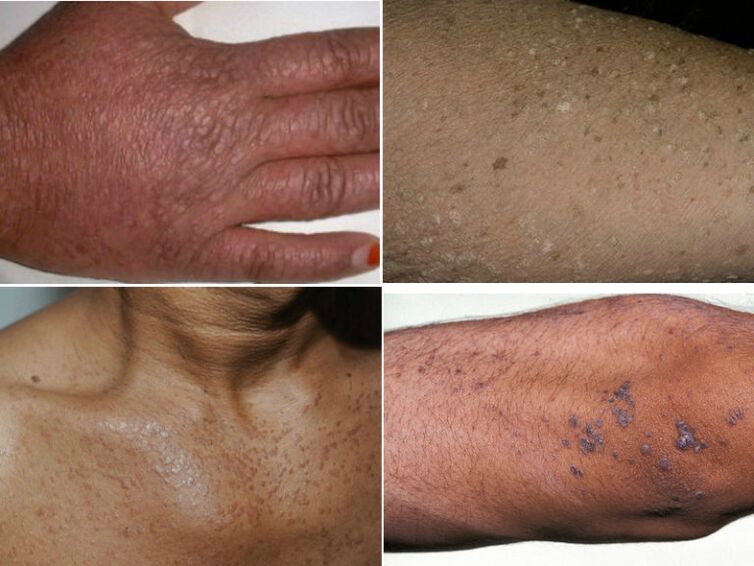
This disease can be confused with vitiligo, so you should consult a specialist. It is transmitted by genetic means, but is very rare in its dermatological form. Outwardly, it resembles an accumulation of flat scaly rashes and age spots. The main localization locations are the face, neck and hands. Unfortunately, this form of warts can develop into cancer.
Warts around mouth
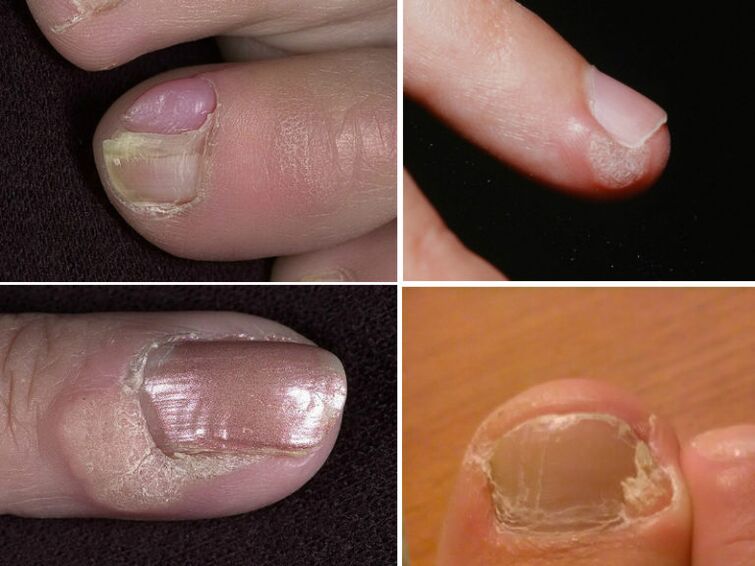
Warts located near the nail destroy the nail plate. They grow deep into the skin and deform the fingers. They do not develop into malignant formations, but this does not make them any less undesirable. Surgery is necessary both for cosmetic reasons and for the health of the fingers.
Bowen's disease
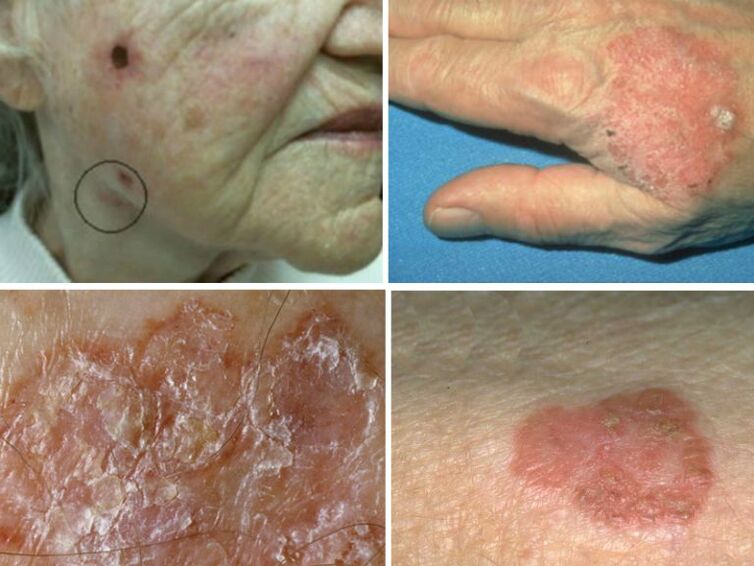
This form of HPV has a tendency to degenerate into squamous cell carcinoma. When the skin is damaged, it will form red spots 5 mm in size, which gradually grow and are covered with scabs. The upper layer of the epidermis is affected, the growth may be up to 5 cm in diameter. It is more common in the elderly, due to impaired immune defenses.
Genital warts
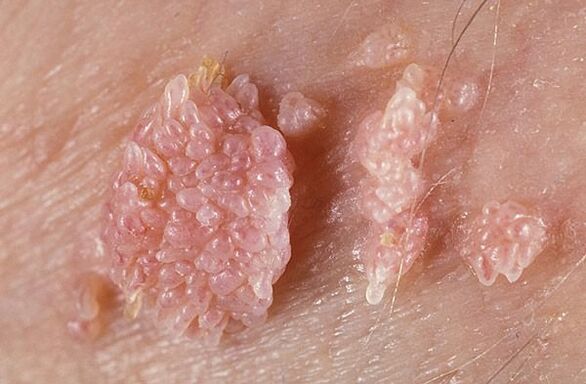
This type of HPV is sexually transmitted, thus affecting the genitals of men and women, as well as the mucous membranes of the urinary and anal systems. The appearance of the shape resembles a cauliflower or a honeycomb. Genital warts can also appear on the corners of the mouth from oral sex. Ingrown parts must be removed because friction can injure them and cause infection.
Papilloma in pharynx
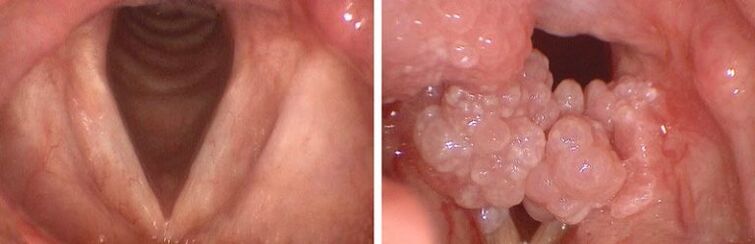
Oral HPV infections are similar to cauliflower. White patches can travel down the lungs and windpipe, making it difficult to breathe. You can injure papillomas while eating, which in turn can lead to cancer. Since a malignant tumor cannot be distinguished from a benign tumor, tests should be performed before the plaques are removed.
The development of papillomatosis is not only found in the elderly. The disease occurs in children and adults. The main signs of laryngeal papillomatosis are dyspnea (speech disorder) and aphasia (inability to speak), hoarseness, and difficulty breathing.
Treatments
Methods for getting rid of papillomavirus infections do not exist today. Therefore, the treatment only reduces the removal of foreign formations and inhibits the virus in the patient's body. There are cases where some viruses die on their own in the body for several years. Methods and preparations to be used for treatment are determined by the physician only on the basis of the patient's diagnosis, examination and external examination.
Destruction method:
- surgical removal (removal) of warts/papillomas (used only if malignancy is suspected);
- coagulation - cauterization formation with a coagulant through which an electric current flows;
- cryodestruction - destruction of warts with liquid nitrogen;
- laser treatment - affects the formation of the laser beam;
- radiofrequency method - exposure of warts/papillomas with a surgical device.
Chemical treatment:
- cauterization with salicylic acid;
- educational processing of trichloroacetic acid concentration of 50-90%;
- acid mixture - treat with an educational preparation (very low effectiveness).
To activate the immune system and suppress the HPV virus, drugs with antiviral and immunomodulatory effects must be included in the therapy.
Disease prevention
It is quite difficult to avoid getting infected with HPV, because this virus can be infected in bathrooms, swimming pools, when sharing household items, in hospitals. But these strains are mild and do not cause cancer. Prevention usually includes personal hygiene, prompt treatment of cuts and wounds with antibacterial agents, and the use of protective equipment during work.
Special attention should be paid to the prevention of sexually transmitted viruses. Protecting the body with a condom is not necessarily successful. Viral infections in sexual partners can be located near the genitals and in the mouth. The best way to avoid infection is to get vaccinated first. Girls and boys should be vaccinated before starting sexual activity between the ages of 11-13. Immunity lasts 3-5 to 10 years and depends on the vaccine and the virus. The injection can then be repeated if there is a risk of infection (change of sexual partners).
High-risk carcinogenic HPV can actually cause changes in tissues and lead to a cancerous process. But several years pass between the first signs and the development of cancer. So it's important to have an annual check-up with your doctor, especially for women. Routine gynecological examination detects changes in both the external genitalia and the cervix. Monitor your health!

























